BACKGROUND: The prognosis of patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) varies depending on the presence of mutations in the FLT3 tyrosine kinase. Internal tandem duplications (ITD) and mutations in the tyrosine kinase domain (TKD) result in continuous activation of FLT3, leading to uncontrolled blast proliferation. Since the publication of the clinical trial CALGB 10603 (RATIFY), it has been established that adding midostaurine to intensive chemotherapy improves the overall survival (OS) of patients with mutated FLT3. However, it is worth noting that this study only included patients 18-59 years old. Subsequently, a phase II clinical trial (AMLSG 16-10 trial) conducted a subgroup analysis suggesting that midostaurine may also benefit to patients between 60 and 70 years of age. Nevertheless, these findings have not been studied in real-world clinical practice.
METHODS : This is multicentric non-interventional retrospective real-world study including patients ≥60 years of age with newly diagnosed FLT3-mutated AML treated with intensive chemotherapy and midostaurine (50 mg orally twice daily, d8-22) between 1st 2017 and July, 30 th 2021 from the French Innovate Leukemia Organization (FILO) and the Programa Español de Tratamientos en Hematología (PETHEMA). The primary objective was to evaluate the efficacy of midostaurine in combination with intensive chemotherapy in patients over 60 years old. We assessed the rate of complete remission (CR) or complete remission with incomplete hematologic recovery (CRi) after induction therapy, OS and event-free Survival (EFS).
RESULTS: A total of 191 patients (FILO Group 122 (63.9%); PETHEMA Group 69 (36.1%)), aged between 60 and 77 years, were enrolled in the study. The patients had a median age of 67.8 years (range 60.1; 77.6). Among them, 134 (70.2%) were aged less than 70 years, while 57 (29.8%) were aged 70 years or older. 159 (83.3%) had a performance status (ECOG) of 1 or lower, while 24 (12.6%) had an ECOG of 2 or higher.
151 (79.1%) had de novo acute myeloid leukemia (AML), and 40 (20.9%) had secondary AML at diagnosis. The median white blood cell count at diagnosis was 26.5 x 10^9/L [5.99; 107]. The median percentage of blasts in the bone marrow at diagnosis was 76% [55; 88.5]. The frequency of FLT3-ITD mutation was 154 (80.6%), FLT3-TKD mutation was 44 (23%), and double mutations were observed in 7 (3.7%) patients. The median FLT3 ITD/wt ratio was 57% [22.5 - 78]. 119 (62.3%) were NPM1 muted.
Regarding the intensive chemotherapy schedule in induction, 162 (84.8%) patients were treated with idarubicin-based regimens, 18 (9.4%) with daunorubicin-based regimens, and 8 (4.2%) with CPX-351. After induction, 150 (78.5%) of the patients achieved complete remission/complete remission with incomplete hematologic recovery (CR/CRi).
Of those patients, 96 (64%) proceeded to intensive chemotherapy schedule in consolidation, with 83 (86.5%) of them receiving midostaurine. In contrast, 32 (21.3%) received non-intensive chemotherapy consolidation, with 27 (84.4%) receiving midostaurine. Additionally, 37 (24.7%) of the patients who achieved CR/CRi after induction underwent a hematopoietic-cell transplantation (HCT), with 33 (89.2%) undergoing allogeneic HCT and 4 (12.1%) undergoing autologous HCT.
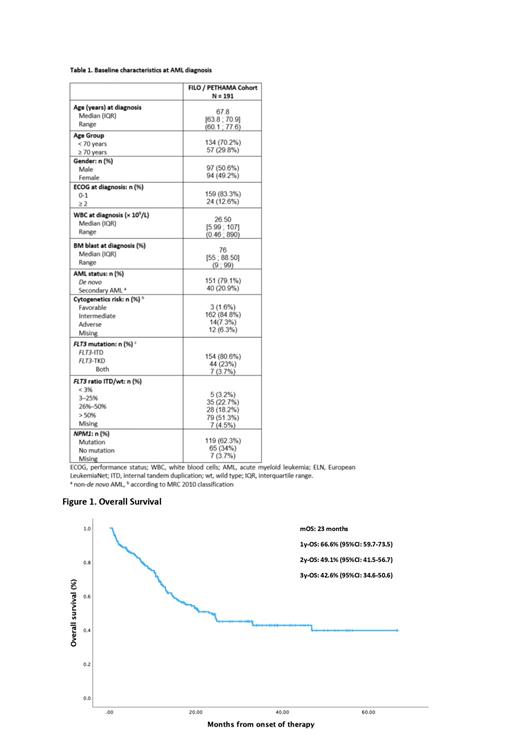
The median follow-up of the patients was 32 months. OS for the entire population was 23 months with a 2-years OS of 49.1% (95%CI: 41.5-56.7). Median EFS for the entire population was 11.1 months with a 2-years EFS of 37.1%. (95%CI: 29.6-44.5). For patients undergoing allogeneic HCT after achieving CR/CRi following induction, the median OS was not reached, with a 2-year OS of 69% (95% CI: 54.6-88.3). In contrast, for patients who achieved CR/CRi after induction but did not undergo allogeneic HCT, the OS was 32.6 months with a 2-year OS of 50.2% (95% CI: 48.4-68.2).
CONCLUSIONS: This real-life study suggests that the addition of midostaurine to intensive chemotherapy regimens in elderly patients could result in acceptable CRc, OS and EFS. In order to establish the benefit of midostaurin, we will compare these results with a historical control cohort.
Disclosures
Bertoli:Novartis: Honoraria; Abbvie: Honoraria, Other: Travel; BMS-Celgene: Honoraria; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria, Other: Travel; Servier: Honoraria; Astellas: Honoraria. Bernal Del Castillo:Otsuka: Consultancy; Jazz: Consultancy; AbbVie: Consultancy. Tavernier:Abbvie: Honoraria. Tormo:AbbVie: Honoraria; MSD: Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria; Astellas: Honoraria; BMS: Honoraria. Pigneux:Astellas: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; BMS: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Roche: Research Funding; Servier: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Support for attending meetings, Research Funding; Abbvie: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Support for attending meetings; Gilead: Honoraria; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Honoraria; Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Montesinos:INCYTE: Consultancy; OTSUKA: Consultancy; Janssen: Speakers Bureau; Astellas: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Consultancy; NERVIANO: Consultancy; GILEAD: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Research Funding; BEIGENE: Consultancy; Ryvu: Consultancy; Kura oncology: Consultancy; Menarini-Stemline: Consultancy, Research Funding; Jazz pharma: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Abbvie: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; BMS: Consultancy, Other, Research Funding; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy, Research Funding. Recher:Abbvie: Honoraria; Amgen: Research Funding; BMS: Other: Personal fees, Research Funding; Astellas: Other: Personal fees; Novartis: Other: Personal fees; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Other: Personal fees, Research Funding; Servier: Other: Personal fees; MaatPharma: Research Funding; IQVIA: Research Funding; Takeda: Other: Personal fees.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal